Dogs may bite their tails due to various reasons, including medical conditions like allergies or infections, behavioral issues stemming from stress or anxiety, and environmental factors such as boredom or lack of stimulation.
You should watch for signs of discomfort, excessive licking, or changes in behavior.
To prevent tail biting, make certain your dog gets regular exercise, mental stimulation, and veterinary check-ups.
Create a calm environment and use positive reinforcement training to redirect the behavior.
If tail biting persists or is accompanied by physical symptoms, consult your veterinarian promptly.
Understanding the underlying causes can help you effectively address and prevent this concerning habit.
Common Causes of Tail Biting

Many dogs engage in tail biting for various reasons, ranging from playful curiosity to serious health concerns. Understanding the common causes of this behavior can help you address the issue effectively.
Tail biting can stem from underlying medical conditions, such as allergies in dogs or skin irritations. It’s crucial to rule out health problems like fleas and ticks, impacted anal glands, or infections that may cause discomfort. If your dog’s tail biting persists, consult a veterinarian to identify any potential medical issues.
Stress and anxiety can trigger compulsive behaviors, including tail chasing and biting. Changes in your dog’s environment or routine may lead to this behavioral problem. Insufficient physical activity and mental stimulation can also result in boredom-induced tail biting.
Some breeds are genetically predisposed to tail-chasing behaviors, which may develop into a habit if not addressed through proper training and intervention. Additionally, attention-seeking behavior can reinforce tail biting, as even negative reactions from owners may encourage the dog to continue.
To prevent tail biting, make certain your dog receives adequate exercise, mental stimulation, and a consistent routine. If the behavior persists, seek professional help to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Identifying Medical Conditions
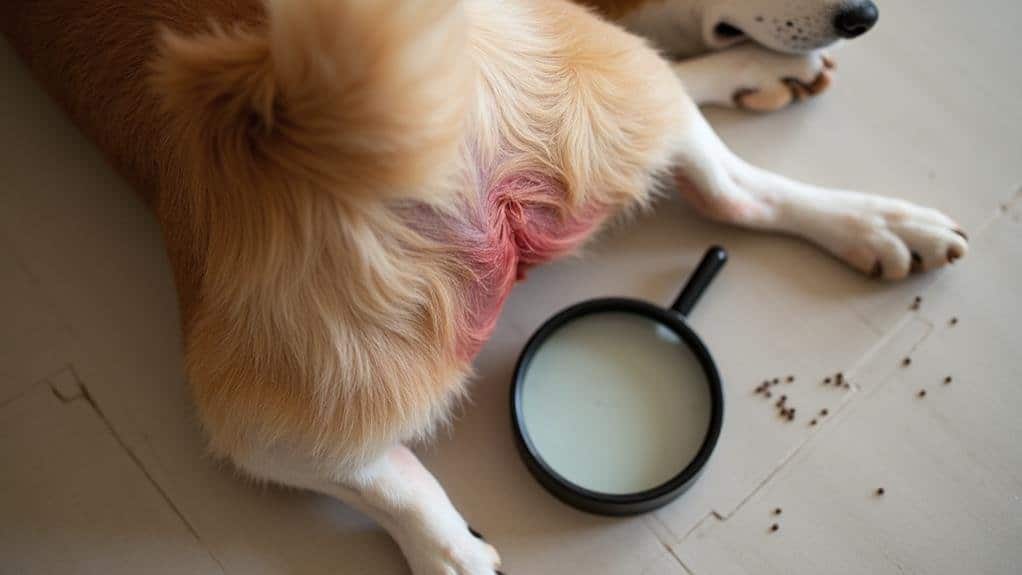
When your dog persistently bites its tail, it’s important to contemplate potential medical conditions as the root cause. Tail biting can be a symptom of underlying causes that require attention.
One common issue is impacted anal glands, which can cause swelling and discomfort, leading to compulsive behavior as your dog seeks relief.
Allergies are another frequent culprit. Whether triggered by food, fleas, or environmental factors, they can cause intense itching and skin irritation, prompting your dog to bite its tail.
Skin infections, including hot spots, may develop from excessive licking and chewing, necessitating prompt veterinary evaluation.
In some cases, neurological issues like partial seizures may manifest as tail biting. To accurately diagnose and treat these conditions, it’s imperative to consult a veterinarian. They can perform a thorough examination to identify the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment.
Regular check-ups are critical for prevention and early detection of health concerns that contribute to tail biting. By staying vigilant and addressing medical conditions promptly, you can help your dog overcome this behavior and improve their overall well-being.
Behavioral Factors and Stress

Three key behavioral factors often contribute to tail biting in dogs: stress, anxiety, and boredom. Your dog may start biting its tail when experiencing stress or anxiety, often triggered by changes in its environment. Moving to a new home or introducing new pets can upset your dog’s emotional balance, leading to this behavior.
Prolonged boredom can also result in compulsive tail biting. When your dog lacks mental stimulation, it may develop repetitive actions as a coping mechanism. To prevent this, it’s essential to identify and address stressors in your dog’s life. Unresolved anxiety can escalate tail biting and lead to other destructive behaviors.
You can considerably reduce the likelihood of tail biting by providing regular exercise and interactive play. These activities offer the necessary physical and mental engagement your dog needs to thrive.
Additionally, implementing training techniques that use positive reinforcement can help redirect your dog’s focus away from tail biting. This approach promotes healthier coping mechanisms in response to stress and anxiety.
Environmental Triggers to Consider

Environmental factors play an essential role in triggering tail-biting behavior in dogs. If you’ve noticed your furry friend engaging in this compulsive behavior, it’s vital to contemplate the impact of environmental changes. Moving to a new home or introducing new pets can increase your dog’s anxiety, potentially leading to tail biting as a coping mechanism.
Your household routine also matters. Fluctuating work schedules can contribute to your dog’s feelings of insecurity and stress, prompting them to seek comfort through tail biting. Additionally, a lack of stimulation from the environment, such as insufficient exercise or interactive play, can lead to boredom. In these cases, dogs may resort to tail biting as a self-soothing mechanism.
External stressors like thunderstorms or fireworks can trigger anxiety in your dog, causing them to engage in tail biting as a way to cope.
To address this issue, focus on creating a calm environment and identifying specific triggers, such as visitors or changes in routine. This approach is vital for effective behavior modification in dogs prone to tail biting.
Preventive Measures and Solutions

To effectively prevent and address tail-biting behavior in dogs, a multifaceted approach is essential. Start by providing your dog with regular physical exercise and mental stimulation. Long walks, playtime, and puzzle toys can greatly reduce boredom-induced tail biting.
Identify and eliminate potential stressors in your dog’s environment, such as changes in routine or new household members, to prevent anxiety-related tail biting.
Don’t neglect regular vet check-ups, as they’re vital for early detection of underlying medical or behavioral causes. Your vet can help diagnose and manage issues like allergies or anal gland problems that may contribute to tail biting.
Implement consistent training using positive reinforcement techniques. Reward desired behaviors and teach a ‘stop’ command to effectively modify tail-biting habits.
Environmental enrichment is another key preventive measure. Provide interactive toys and opportunities for socialization with other dogs to offer mental challenges that deter compulsive tail biting.
When to Consult a Veterinarian

While many cases of tail biting can be addressed through preventive measures, certain situations demand prompt veterinary attention. If your dog’s tail biting behavior persists for more than a few days, it’s vital to consult a veterinarian to rule out underlying medical issues like skin infections or allergies. These persistent behaviors may be signs of discomfort that require professional evaluation.
Watch for signs of distress, such as excessive licking or scooting, as they could indicate anal gland problems or other pain-related issues. If you notice sudden changes in your dog’s behavior, especially increased tail biting due to stress or anxiety from environmental changes, seek a veterinary consultation for behavioral assessment and management.
Don’t ignore physical symptoms like redness, swelling, or discharge around the tail area. These signs warrant immediate veterinary attention to prevent secondary infections.
Regular veterinary check-ups are important in identifying and addressing potential health concerns that may contribute to tail biting behaviors. By staying vigilant and seeking professional help when needed, you’ll guarantee your dog’s overall well-being and address the underlying causes of tail biting effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Prevent a Dog From Biting Its Tail?
To prevent your dog from biting its tail, you’ll need to provide regular exercise, mental stimulation, and a stress-free environment. Use positive reinforcement training, guarantee a balanced diet, and address any underlying health issues with your vet.
Why Are the Tips of Dogs Tails Sensitive?
Your dog’s tail tip is sensitive due to numerous nerve endings. It’s also vulnerable to skin conditions, injuries, and allergies. Some breeds have less protective fur, making their tails more susceptible to external factors like temperature changes or grooming.
Why Is My Dog Chasing and Biting His Tail?
Your dog’s tail chasing could be due to boredom, playfulness, or underlying issues like stress or medical problems. You’ll want to observe when it happens and provide more mental stimulation. If it persists, consult your vet for advice.
Why Won’t My Dog Stop Licking and Biting His Tail?
Your dog’s persistent tail licking and biting could be due to medical issues, anxiety, or boredom. You’ll need to identify the root cause by observing their behavior and consulting a vet. It’s essential to address this promptly for their well-being.
Conclusion
You’ve now learned the various reasons why dogs might bite their tails, from medical issues to behavioral factors.
By identifying the root cause, you’re better equipped to address the problem. Remember, prevention is key. Keep your dog healthy, mentally stimulated, and free from stressors.
If you’re ever unsure or the behavior persists, don’t hesitate to consult your vet.
With patience and proper care, you can help your furry friend overcome this habit.

